In the world of the internet and web development, you’ve probably heard the terms URL and URI being tossed around. Sometimes people use them interchangeably — but are they the same thing? Not exactly.
This article will help you clearly understand the difference between URL and URI, using real-world examples like www.google.com, and break everything down into simple language. Whether you’re a student, a developer, or just a curious browser, this guide is for you!
🔍 What is a URI?
URI stands for Uniform Resource Identifier.
A URI is a generic identifier used to name or locate a resource on the internet — it could be a website, a file, an image, a video, or anything else accessible online.
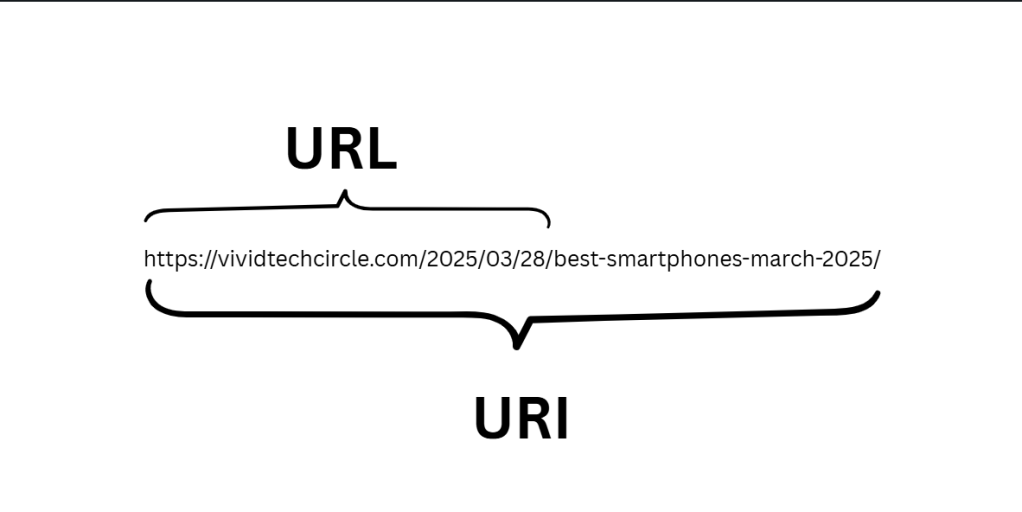
Think of a URI as an umbrella term. It includes both URLs and URNs (Uniform Resource Names).
👉 Definition:
A URI is a string of characters that uniquely identifies a resource either by location, by name, or both.
🔗 Example of a URI:
- https://www.google.com/search?q=chatgpt
- urn:isbn:0451450523
In the above examples:
- The first one is a URL (a type of URI).
- The second is a URN (it names a book but doesn’t tell you where to find it).
🌐 What is a URL?
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator.
It is the most common type of URI and is what we use every day to locate a resource on the web. If you’ve ever typed www.google.com into your browser — that’s a URL.
👉 Definition:
A URL is a type of URI that tells you how to reach a resource using a specific protocol like http, https, ftp, etc.
🔗 Example of a URL:
- https://www.google.com
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=abc123
- ftp://example.com/file.zip
Each of these examples contains:
- A scheme (https, ftp)
- A domain or IP address
- Optional paths, queries, and fragments
✅ Key Differences: URI vs URL
Let’s compare them side-by-side so you can remember easily.
| Feature | URI | URL |
| Full Form | Uniform Resource Identifier | Uniform Resource Locator |
| Purpose | Identifies a resource | Locates a resource |
| Types | Includes URLs and URNs | Only a type of URI |
| Example | urn:isbn:0451450523, https://google.com | https://google.com/search?q=chatgpt |
| Used in Web Browsers | Sometimes (mostly URLs are used) | Always |
🔍 Real-World Examples
Here are some common web examples that are URLs (and thus also URIs):
- 🔎 Google Search:
https://www.google.com/search?q=uri+vs+url
This URL tells the browser to open Google and search for “uri vs url”. - 🎥 YouTube Video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ
The video is located via a URL which is part of the URI system. - 🧾 Amazon Product Page:
https://www.amazon.in/dp/B09V7R2X8T
Again, a URL pointing to the location of a product.
All of these are URLs, and therefore URIs.
🧠 Quick Summary to Remember
- Every URL is a URI, but not every URI is a URL.
- A URI can either locate (URL), name (URN), or both.
- URLs are what you use in your browser’s address bar to open a webpage.
📌 Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between URL and URI might seem technical at first, but it’s a small yet important piece of web literacy. The next time you enter a web address or debug a piece of code, you’ll know exactly what you’re working with!
Whether you’re a beginner in web development, learning about HTTP and internet protocols, or just expanding your digital knowledge, this fundamental concept will always be useful.
Leave a comment